VISION
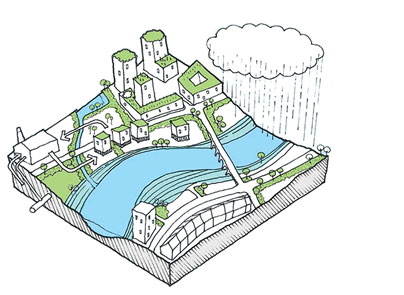
Making Ganga basin cities water-sensitive for improved river health
AIM
Capacity building initiatives, action research and developing model projects for making cities in the Ganga basin water-sensitive, by improving the river flow and health with water-sensitive urban design and planning.
KEY THEMATIC AREAS
Over the years, the groundwater levels in the basin have deteriorated, primarily in the urbanized areas of upper Ganga basin, along the rivers Ganga and Yamuna. These rivers lose a lot of their flow to recharge the depleted groundwater. There is extreme groundwater stress with depleting groundwater table, and most urban areas in the basin have been categorized as ‘overexploited’, ‘critical’ or ‘semi-critical’. ‘Overexploited’ signifies that more groundwater is extracted than what is recharged, ‘critical’ means groundwater taken out is 90–100 per cent of what is recharged, and ‘semi-critical’ implies an extraction rate of 70–90 per cent. There is a need to focus on extensive groundwater recharge in urban areas in order to contribute to the flow of the rivers and streams, which will also help in reducing the concentration of pollutants.
This comprehensive vision will be achieved through five key thematic focus areas:
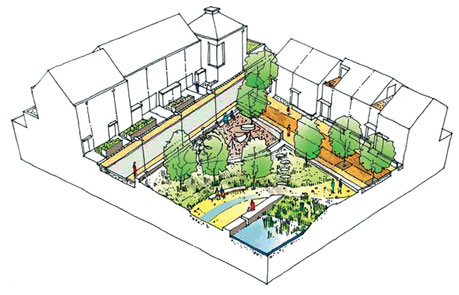
The programme with water-sensitive urban design and planning approach aims to integrate these five key thematic focus areas and offers a blueprint to implement as well as monitor them.
OBJECTIVES
- Sensitize and build capacities of 1,300+ municipal and state functionaries, elected representatives and other key actors as well as the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) team in making cities water-sensitive.
- Help improve convergence of programmes like Jal Jeevan Mission, Atal Bhujal Mission, Jal Shakti Mission, Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) and Swachh Bharat Mission.
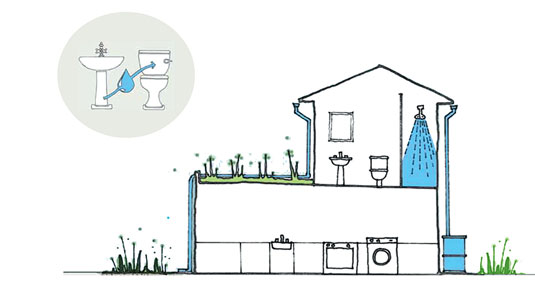
To improve capacities and understanding about issues of decentralized water management and augmenting water supply through rainwater harvesting, decentralized sewage including septage management and reuse or recycling of wastewater.

To secure sustainability in urban water management for improved river flow and health.

To increase knowledge about best practices regarding sustainable water and wastewater management including rainwater harvesting; sewage treatment; reuse and recycling of wastewater; water efficiency; and conservation, protection and management of urban water bodies;
1300+ number state / municipal functionaries and other sector players involved in promoting sustainable urban water management.
40+ activities over 3 years - 24 Training (incl. 12 no. online), 12 webinars, annual knowledge conclaves including field exposure visits
Practitioner’s Guide (5 nos.)
- Urban Groundwater Management
- Urban Water Bodies Management
- Decentralised Wastewater Treatment and Local Reuse
- Planning & Designing Water Sensitive Cities for improved river flow/ health
- Water Sensitive Cities Index for ranking in Ganga Basin Cities
Helpdesk & Web portal for handholding support to design and implement model WSUDP intervention as model projects in select 4-6 cities as learning centers.
TARGET AUDIENCE
- State and municipal functionaries dealing with urban planning, water, sewerage and sanitation including the flood and drainage sectors in Ganga basin states
- State Programme Management Group (SPMG), Programme Management Units and Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) supporting state and cities
- Namami Gange Programme partners and key funding agencies—World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB) and other bilateral funding agencies
- International Non-Governmental Organization and local grassroots community-based organization including self-help groups
- Technology providers, consultants including practitioners, researchers, academicians and NGO’s promoting sustainable water management